Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) is designed to create entirely new and original content, including text, images, audio, code, and even complex simulations. Unlike traditional AI systems that process and retrieve existing data, GenAI is capable of producing innovative outputs, positioning it as a key driver of transformative change across industries. In the world of autonomous vehicles (AVs), this creative power is not just an enhancement, it’s a breakthrough.
In the realm of autonomous vehicles (AVs), GenAI is reshaping how these systems operate and evolve. Its ability to interpret and generate multimodal data—combining sensor inputs, visual information, and language—enables smarter decision-making, enhances passenger experiences, and accelerates advancements in safety and efficiency.
From improving perception systems to enabling real-time, personalized in-vehicle interactions, GenAI plays a foundational role in next-generation transportation. This article explores how GenAI is accelerating innovation in autonomous vehicles, driving smarter systems, safer roads, and more personalized user experiences.
What Sets Generative AI Apart?
Before diving into its impact on AVs, let’s understand what makes GenAI different from traditional AI:
- Original Content Generation: GenAI models are trained on vast datasets to generate entirely new outputs, excelling at “creating,” whether it’s producing natural language, designing vehicle interfaces, or interpreting environmental data in real time. For AV systems, GenAI can generate synthetic sensor data or visual content. This kind of content generation is vital when real-world data is unavailable or incomplete. High-quality, annotated data is essential for training robust GenAI models.
- Contextual Understanding: These models excel in understanding nuanced context, intent, and data relationships. For example, in autonomous vehicles, a GenAI model could not only interpret spoken commands but also predict likely follow-ups, offering a seamless passenger experience.
- Multimodal Capabilities: Combining various data types, such as sensor inputs, language, text, and images, is key for more accurate and intelligent vehicle responses. Data annotation for model training helps optimize AV performance. With tools like Codex and text-to-image models, GenAI combines different data types into cohesive outputs, making it invaluable for autonomous vehicle systems where decision-making relies on synthesizing visual, spatial, and textual data.
Popular examples include large language models like GPT-3, text-to-image generators like DALL-E, and code-generation tools like Codex. These models have demonstrated impressive abilities to assist humans with various creative and analytical tasks. However, GenAI also raises important questions about the ethical use of these powerful technologies.
Why Generative AI Matters for Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on vast amounts of data for decision-making, perception, and real-time responses. GenAI introduces new opportunities to leverage AI in previously unimaginable ways, thereby accelerating the development and deployment of autonomous vehicle (AV) technologies.
- Corpus Creation: GenAI enables the generation of large, diverse datasets or corpora, such as images or sensor data, to train AV models. This helps AV systems improve recognition accuracy in edge cases, where real-world data may be difficult or expensive to obtain. GenAI can also generate valuable data for AV model training, especially for rare or edge-case scenarios.
- Advanced Testing and Simulation: GenAI can create dynamic, simulated environments that replicate a wide range of real-world driving scenarios. This allows AV developers to test their systems in diverse conditions and situations without relying solely on real-world trials. This drastically cuts development time and cost.
- Predictive Decision-Making: With its ability to analyze patterns and infer behavior, GenAI improves how AVs anticipate road situations like a pedestrian stepping off a curb or a vehicle merging suddenly.
- Human-Machine Interaction: GenAI powers natural, conversational interfaces between AVs and passengers, enabling voice commands, route preferences, and in-vehicle personalization.
- Bias and Explainability: By identifying skewed training inputs, GenAI helps reduce bias in decision-making. Its explainable outputs also improve transparency, making AVs more trustworthy.
Core Technologies Behind Autonomous Mobility
Autonomous mobility refers to the development of vehicles and transportation systems that can operate without direct human control or supervision. The key technologies enabling autonomous mobility include:
- Sensors: Advanced sensors, such as cameras, radar, LiDAR, ultrasonic sensors, and 3D sensors, perceive the vehicle’s surrounding environment, collecting critical data in real-time.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML): These algorithms process sensor data, detect and classify objects, and make complex decisions about vehicle navigation and control.
- Processing Power and Edge Computing: Autonomous vehicles are essentially supercomputers on wheels, equipped with powerful chips that process vast amounts of environmental data in real time at the edge. This edge processing capability is vital for making split-second decisions on dynamic roads where safety and efficiency depend on immediate responsiveness.
- Automated Driving Systems: Sophisticated software integrates sensor data, AI/ML models, and vehicle controls to execute dynamic driving tasks without human intervention.
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication: Connected cars maintain constant communication with other vehicles, infrastructure, pedestrians, and cloud services. This always-on connectivity leverages cloud-based applications and processes to enhance real-time updates, coordination, and overall autonomous vehicle functionality.
Together, these technologies enable autonomous mobility to navigate complex, dynamic environments while maintaining safety, efficiency, and adaptability.
Benefits of Autonomous Mobility
Autonomous mobility brings transformative potential to transportation systems, offering benefits that extend beyond individual convenience to societal and environmental impacts:
- Improved Safety: By reducing human errors such as distractions, fatigue, and impaired driving, autonomous vehicles significantly enhance road safety.
- Enhanced Mobility: Offers greater accessibility to individuals who cannot drive, including the elderly, people with disabilities, or those unable to afford an automobile.
- More Efficient Transportation: Optimizes traffic flow and reduces congestion through real-time data analysis and route optimization.
- Reduced Traffic Congestion: Advanced systems manage vehicle spacing and streamline navigation to avoid bottlenecks.
- Lower Fuel Consumption and Emissions: Efficient driving patterns reduce idle time and fuel usage, contributing to a greener environment.
Key use cases for autonomous mobility
Autonomous mobility applications span various industries, showcasing the versatility and impact of this technology:
- Self-Driving Consumer Vehicles: Personal vehicles equipped with autonomous driving capabilities provide safer and more convenient transportation options.
- Autonomous Shuttles and Buses: Facilitate public transportation by offering reliable and efficient services in urban and rural areas.
- Autonomous Trucks and Delivery Vehicles: Streamline logistics by optimizing routes and ensuring timely deliveries of goods and packages.
- Autonomous Construction and Mining Equipment: Improve safety and productivity in challenging environments by automating heavy machinery operations.
Major companies and tech players working on autonomous mobility include Waymo, Cruise, Tesla, Baidu, Zoox, Aurora, and many traditional automakers. While significant progress has been made, widespread adoption of fully autonomous vehicles still faces technical, regulatory, and public acceptance challenges that need to be addressed.
Generative AI and Autonomous Vehicles
The convergence of generative AI and autonomous vehicles is poised to revolutionize the transportation industry. By leveraging the power of AI to generate realistic and diverse data, AV developers can significantly accelerate the development and deployment of safer and more efficient self-driving cars.
Key Areas of Impact for GenAI in Autonomous Vehicles:
External to the AV:
- Realistic Virtual Environments: GenAI can create highly detailed virtual environments that simulate real-world driving conditions, including diverse weather patterns, traffic scenarios, and unpredictable obstacles. These simulations can help train AV systems to handle a wide variety of conditions.
- Data Augmentation: GenAI generates synthetic data to expand training datasets, improving the robustness of AI models. This synthetic data can address edge cases—situations that are difficult or costly to capture in the real world, ultimately helping AVs respond effectively to a range of unforeseen driving situations.
Internal to the AV:
- Data Cost, Latency, and Freshness: The real-time operation of AVs relies heavily on the freshness of the data they process, such as maps, traffic updates, sensor inputs, and in-cabin monitoring systems like driver monitoring or passenger behavior tracking. Latency in retrieving and processing this data can lead to delayed decisions and potential safety risks.
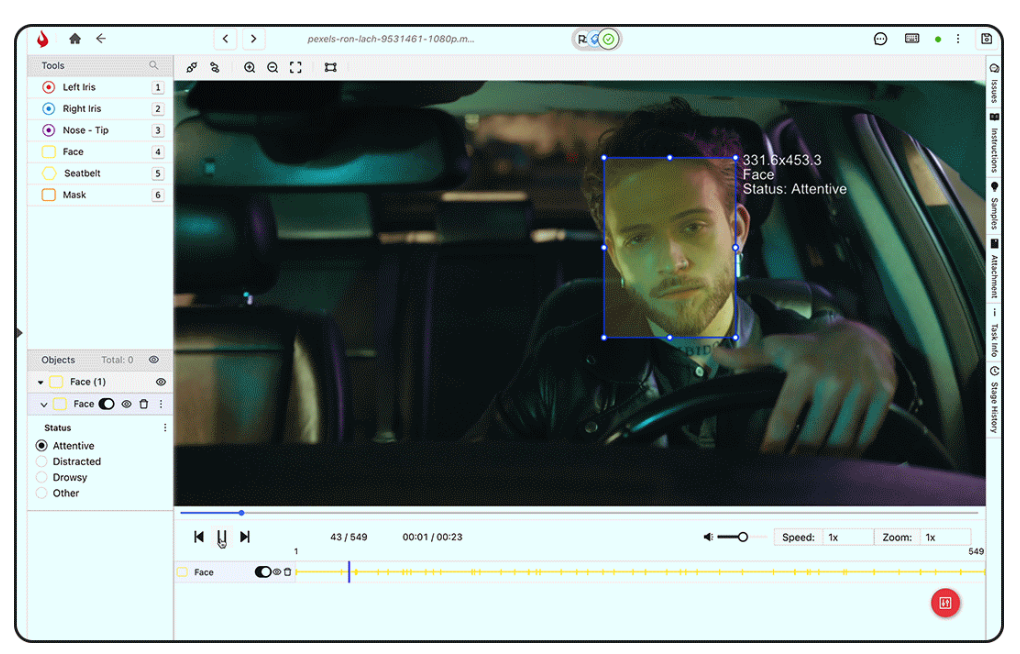 GenAI can help mitigate these issues by generating up-to-date, synthetic data and improving decision-making speed, thereby reducing the need for expensive or delayed data. The cost and efficiency of obtaining real-time data (like live maps, traffic conditions, or in-cabin sensor inputs) can also be optimized through GenAI-driven data synthesis and predictive analytics.
GenAI can help mitigate these issues by generating up-to-date, synthetic data and improving decision-making speed, thereby reducing the need for expensive or delayed data. The cost and efficiency of obtaining real-time data (like live maps, traffic conditions, or in-cabin sensor inputs) can also be optimized through GenAI-driven data synthesis and predictive analytics. - Improved Perception and Decision-Making:
- Real-time Scene Understanding: GenAI can help AVs better understand complex traffic scenarios by generating accurate predictions of pedestrian and vehicle behavior.
- Advanced Object Detection and Tracking: By analyzing vast amounts of visual data, GenAI can enhance the ability of AVs to identify and track objects, such as pedestrians, cyclists, and other vehicles, even in challenging conditions.
- Natural Language Processing: GenAI can enable more intuitive and natural interactions between humans and AVs through advanced voice commands and conversational interfaces.
- Personalized Experiences: By analyzing user preferences and behavior, GenAI can tailor the in-vehicle experience to individual needs, creating a more comfortable and enjoyable ride.
- Bias Mitigation: GenAI can help identify and mitigate biases in training data, ensuring that AVs make fair and unbiased decisions.
- Explainable AI: By providing insights into the decision-making process, GenAI can enhance transparency and accountability in AV systems.
Applications for GenAI in Autonomous Mobility
Generative AI (GenAI) transforms autonomous mobility by delivering practical, user-focused solutions that enhance safety, efficiency, and adaptability. By leveraging its advanced capabilities, GenAI enables the following high-impact applications:
- Smarter Scene Interpretation: GenAI empowers autonomous vehicles to better understand complex driving environments, from adverse weather to chaotic traffic, ensuring robust navigation without relying solely on real-world trials.
- Proactive Navigation: GenAI anticipates road dynamics, such as pedestrian movements or sudden traffic shifts, enabling vehicles to make safer, more efficient decisions in real time.
- Tailored Passenger Comfort: GenAI customizes in-vehicle settings—like temperature, lighting, or media—based on individual preferences, creating a seamless and enjoyable ride.
- Safe Testing Environments: GenAI creates diverse, virtual driving scenarios to rigorously test autonomous systems, reducing risks and costs associated with real-world experiments.
- Intuitive Passenger Interaction: With natural, responsive voice interfaces, GenAI makes vehicle interactions effortless, adapting to passengers’ preferences and needs.
These applications position GenAI as a cornerstone of autonomous mobility, accelerating the development of safer, smarter, and more user-centric transportation solutions.
Challenges and Path Forward:
While the potential of GenAI in AV development is immense, several challenges remain:
- Data Quality and Diversity: GenAI models rely on high-quality, varied datasets to perform effectively. Poor data can lead to unreliable outcomes, necessitating robust curation, as provided by partners like iMerit.
- Computational Demands: Training large-scale GenAI models requires significant processing power, posing cost and infrastructure challenges for developers.
- Ethical Considerations: Privacy concerns, such as protecting passenger data, and fairness in crash decisions, like prioritizing pedestrian safety, must be addressed to maintain public trust.
Despite these challenges, the future of AVs remains bright. By embracing the power of GenAI, the development of safer, more efficient, and more accessible transportation solutions can be accelerated.
Conclusion
Generative AI and autonomous mobility are reshaping the transportation landscape, offering safer, more efficient, and accessible mobility solutions. These technologies lay the groundwork for a future where vehicles not only navigate complex environments autonomously but also interact seamlessly with humans and infrastructure.
iMerit’s expertise in data curation, annotation, and evaluation ensures that high-quality datasets power these advancements, driving the industry toward precision and scalability.
By leveraging iMerit’s specialized services and the advanced capabilities of Ango Hub, businesses can accelerate the development of cutting-edge autonomous mobility solutions with greater efficiency and accuracy.
The road to truly intelligent mobility is being paved, and GenAI is in the driver’s seat.

























