Autonomous vehicles (AVs) are becoming more capable every day, but how do they truly get road-ready? Beyond test tracks and real-world miles, much of their “learning” happens in virtual environments. And not just any simulations, data-driven simulations built from the messiness, unpredictability, and nuance of the real world, where the bottleneck isn’t physics or dynamics but the right labeled data.
This is where (DDADS) comes in.
What Is Data-Driven Simulation for Autonomous Vehicles?
Traditional AV simulation relies heavily on synthetic or manually constructed traffic scenarios. While these are useful for early-stage validation, they often lack the complexity, variability, and unpredictability of real-world driving environments.
DDADS flips this approach, using real-world sensor data captured from vehicles on the road and transforming it into simulation-ready scenarios. The key is not just capturing the data, but annotating, curating, and governing it so that every edge case, rare interaction, and behavioral nuance is represented for downstream evaluation and training.
The goal? To recreate real-world complexity with all its corner cases: poorly marked roads, aggressive merges, distracted pedestrians, sudden obstructions, and unpredictable weather.
The result: Simulations that don’t just test AVs, but train them to handle reality.
Why Real-World Data Matters in Simulation
AV systems thrive on edge cases, those rare, unexpected moments that define safety and performance. But those same moments are hard to plan for in traditional simulations. That’s where real-world data shines:
- Captures long-tail edge cases: from a scooter darting into traffic to a double-parked delivery van in a bike lane.
- Offers authentic variation: in weather, lighting, road conditions, and driver behaviors.
- Regional quirks: such as jaywalking norms, rickshaws in India, or unmarked rural intersections in the U.S.
When annotated and curated properly, this data forms the foundation for scenario mining, counterfactual perturbation, and coverage-tracked simulation pipelines, all overseen by iMerit experts to ensure high-fidelity inputs for AV testing.
The Building Blocks of iMerit-Powered DDADS
iMerit’s core contribution is the data and evaluation loop, scenario mining, ground truth annotation, edge-case curation, coverage accounting, and human-in-the-loop QA. Here’s how it works:
Multimodal Sensor Fusion & Ground Truth Annotation
Simulations must accurately reflect inputs from LiDAR, radar, cameras, IMUs, and GNSS. iMerit annotators create synchronized 3D bounding boxes, trajectories, segmentation masks, and occlusion handling for all relevant sensors. Time-sync offsets and calibration cues are labeled so simulation engineers can calibrate sensor realism.
Scenario Mining and Descriptor Creation
From terabytes of driving footage, iMerit mines clips triggered by TTC, PET, deceleration spikes, or policy violations, clusters recurring patterns, and writes scenario descriptors with deterministic IDs, actor metadata, map references, and seeds for reproducibility. These descriptors provide a standardized, engine-agnostic way to represent complex scenarios, capturing actors, sensors, ground truth, and evaluation oracles.
Example Scenario Descriptor (JSON)
{
“scenario_id”: “cutin_freeway_2025_06_14_07”,
“map_id”: “metro_v12”,
“seed”: 421337,
“actors”: [
{“id”: “veh_12”, “type”: “car”, “intent”: “cut_in”, “aggression”: “0.7”}
],
“sensors”: {
“lidar_roof”: {“rpm”: 1200},
“cam_front”: {“rolling_shutter”: true}
},
“gt”: {
“bbox3d”: true,
“tracks”: true,
“segm”: true,
“occlusion_masks”: true
},
“oracles”: {“rss_min_ttc_s”: 2.0, “jerk_max_mps3”: 4.0}
}
Behavior & Intent Tagging
It’s not just objects; annotators label intent, aggression, courtesy, gap acceptance, and “unnatural” activities to fuel interactive agent simulations.
Counterfactuals and Edge-Case Libraries
iMerit experts define valid perturbation ranges (minimal-edit constraints), human-check counterfactual scenarios, and maintain curated edge-case libraries with pass/fail oracles. This ensures rare or high-risk interactions are tested under plausible variations.
Coverage Accounting & Active Learning
Scenario taxonomy labels track road class, intersection type, actor mix, visibility, friction, speed, and intent. Coverage dashboards identify gaps, prioritize risk-weighted sampling, and feed failures back to training and mining pipelines.
Governance & Provenance
All annotations follow strict data governance: PII redaction, surrogate keys, audit trails, lineage per label (who, when, which rubric/tool version), inter-rater calibration, and QA sampling plans.
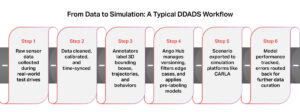
From Data to Simulation: Typical Workflow
- Raw sensor data collected during real-world test drives
- iMerit annotators clean, calibrate, and time-sync the data
- Label 3D bounding boxes, trajectories, and behaviors, including intent tags
- Scenario descriptors created and edge cases flagged; Ango Hub manages versioning and pre-labeling automation
- Simulation-ready packages exported for engines like CARLA
- Golden sets and oracles are maintained; failures feed back into mining and labeling
This tight, human-in-the-loop loop ensures that simulation evolves alongside AV software, with reproducible, traceable, and coverage-aware data.
Technical Challenges in Annotation & Data Governance
- Replay Divergence
Pure log replays collapse when the ego vehicle deviates. To maintain realistic interactions, semi-reactive labels and constraints are needed. Annotators ensure that these scenarios remain plausible, flagging unnatural agent behaviors and documenting conditions for downstream model evaluation. - Sensor Realism
Simulations are only as good as the sensor fidelity they emulate. Annotators create occlusion masks, material cues, and time-sync labels to allow simulation engineers to calibrate LiDAR, camera, and radar data accurately. Without precise data labeling, sensor artifacts can introduce false confidence or hidden blind spots. - Coverage Illusion
Running thousands of near-duplicate scenarios can give a false sense of safety. Data labeling teams maintain taxonomy labels and parameter dispersion metrics, helping engineers identify underrepresented scenarios and ensuring diverse coverage across rare edge cases. - Oracle Drift
Composite safety, comfort, and rule compliance metrics depend on consistent ground truth. Human-in-the-loop rubrics and adjudication during labeling prevent drift in oracles over time and support repeatable closed-loop evaluation. - Data Labeling and Governance
High-quality data labeling is critical for simulation reliability. Teams manage PII redaction, surrogate key generation, provenance tracking, inter-rater calibration, and audit trails. Properly governed and labeled datasets ensure that edge cases, counterfactuals, and regression scenarios feed back into training pipelines safely and effectively. - Scalability and Traceability
Thousands of hours of multi-sensor data must be annotated, validated, and version-controlled. Workflow orchestration platforms like Ango Hub support labeling pipelines, track who did what and when, and maintain lineage across scenarios, ensuring reproducibility and traceability for safety audits.
The Future: Smarter, Safer, Faster AVs
As AV development scales across cities, geographies, and regulatory environments, iMerit-powered DDADS ensures teams have a deterministic, traceable, and risk-weighted data foundation. Generative AI can further expand scenario variants, but the base remains rich, curated, high-quality ground truth from human annotators.
Programs like iMerit Scholars are preparing the next generation of data specialists, equipping them to work on AV data challenges and contribute to smarter simulation pipelines. Join now
Conclusion: Simulation-Ready Starts with Data-Ready
Data-driven simulation is only as effective as the annotated, curated, and governed data behind it. iMerit transforms raw logs into high-fidelity 3D annotations, behavior labels, edge-case libraries, and coverage-aware scenario descriptors.
We partner with AV developers moving from handcrafted simulations to data-informed pipelines, where every near-miss, unexpected stop, or tricky merge becomes a reproducible scenario that vehicles can learn from virtually.
At iMerit, we make simulation-ready possible. With advanced 3D sensor fusion annotation tools, human-in-the-loop workflows, and a flexible platform like Ango Hub, we help leading AV companies turn raw, unstructured data into curated, high-impact simulation scenarios.

























