As generative AI models become increasingly capable, they also become increasingly unpredictable. Even when models avoid factual errors or offensive content, they often still “miss the vibe”, delivering responses that are subtly off-tone, culturally insensitive, overly confident, or simply untrustworthy.
Welcome to the era of vibe hacking: the process of proactively testing and tuning AI outputs to ensure they align not just with rules and logic, but with human expectations, tone, intent, and trust. It’s an extension of red-teaming, and it’s essential for the responsible deployment of GenAI.
Understanding Vibe Hacking in AI
Vibe hacking refers to adversarial techniques that exploit a generative model’s tone, subtext, and emotional cues rather than its surface-level logic or syntax. It’s the practice of probing a model for ‘how’ it says things, not just ‘what’ it says.
While traditional red-teaming focuses on jailbreaks and factual hallucinations, vibe hacking explores failures like:
- Overconfidence in high-risk domains (e.g., health or finance)
- Tone misalignment (e.g., being cheerful in a serious context)
- Culturally inappropriate or stereotypical responses
- Manipulative or suggestive subtext
These failures don’t always show up in factual QA. They require nuance, context, and emotional awareness, making them especially dangerous and difficult to detect.
From Threat to Trust: Why Vibe Hacking Matters
Vibe hacking isn’t just a cybersecurity threat. It’s a trust failure. Whether you’re building a medical assistant, a financial advisor, or a brand chatbot, the model’s tone is the user experience.
Unaligned tone can:
- Erode user confidence
- Introduce legal or ethical risk
- Create viral PR disasters
Preventing those outcomes requires more than filters—it requires design. And that starts with testing.
The Evil Twin of Vibe Coding
If you have heard of vibe coding, you are already familiar with its promise: creating AI applications by expressing intent in natural language. Say what you want, and the model builds it.
But vibe hacking is its “evil twin”, using similar language-based prompting and tone manipulation to mislead, exploit, or deceive. According to experts, this is where generative models become cybersecurity risks:
- Malicious actors use emotionally persuasive prompts to write phishing emails.
- AI-generated malware is built from harmless-sounding queries.
- Social engineering attacks become personalized and emotionally attuned.
Vibe hacking tools like WormGPT and FraudGPT are now being used to create convincing phishing messages, deepfake scams, and even autonomous AI agents capable of identifying and exploiting vulnerabilities. These aren’t hypothetical threats; they’re active and evolving.
Red-Teaming for Vibe: A New Approach
Vibe hacking deserves a structured, proactive response. That’s why we treat it as a specialized form of red-teaming, one that:

- Uses prompt perturbation to generate fringe behavior
- Involves multi-turn dialogues to simulate evolving tone
- Leverages domain experts and culturally diverse annotators to flag nuanced risks
- Captures disagreement, interpretation, and subjective annotation across reviewers
Red-teaming for vibe ensures your model doesn’t just avoid “bad outputs”; it aligns with emotional and contextual expectations.
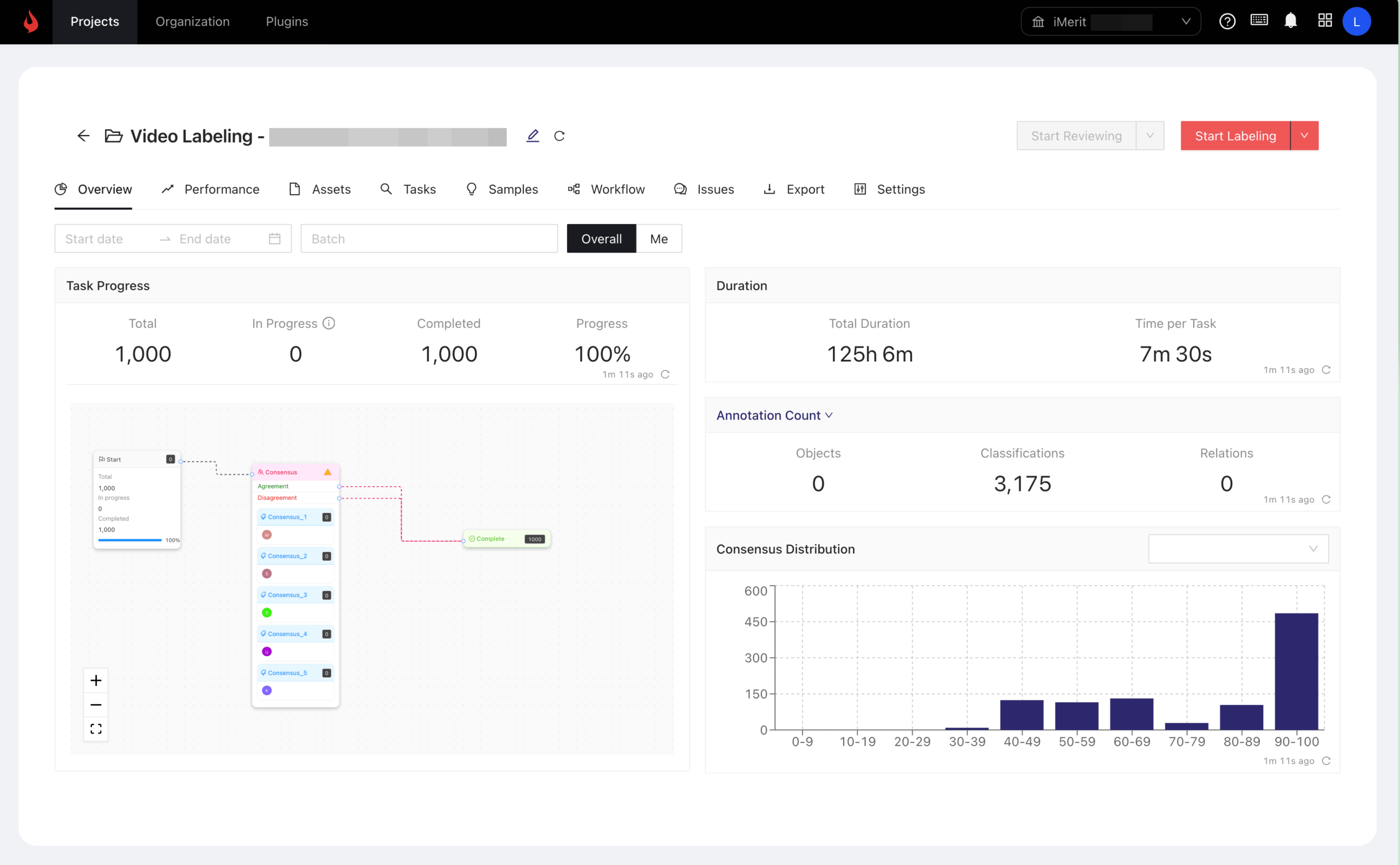
Ango Hub: Built for Red-Teaming at High Volume and Complexity
Vibe hacking requires more than catching jailbreaks or hallucinations—it demands infrastructure built for nuance, subjectivity, and scale. That’s where iMerit’s Ango Hub comes in: a platform purpose-built to support complex red-teaming workflows that target tone, subtext, and emotional alignment.
- Tone and subtext tagging: Custom tag sets allow annotators to flag emotional cues, tone shifts, and suggestive language.
- Disagreement management: Because vibe is subjective, Ango Hub enables multiple reviewers to submit, compare, and resolve conflicting annotations.
- Multi-turn context support: Red-teaming rarely happens in isolation. Ango Hub supports full conversation histories to assess tone evolution.
- Analytics and trends: Clients can track which tone issues are recurring, which prompts provoke misalignment, and how model behavior changes over time.
- Scenario testing: Ango Hub enables structured evaluations across defined user journeys and edge cases, helping assess model performance in real-world and high-risk contexts. These tests simulate multi-step interactions, revealing failures in tone continuity, emotional awareness, and escalation handling, especially in sensitive applications like healthcare or legal advice.
- Bias detection: Using diverse expert reviewers and annotation workflows, Ango Hub surfaces implicit bias, stereotyping, and harmful assumptions in model responses. Reviewers are trained to evaluate subtextual bias and intersectional harm, allowing teams to isolate not just what the model says, but how it may reflect unconscious societal patterns.
- Custom asset support: Teams can upload and integrate proprietary test cases, domain-specific prompts, and regulatory datasets to challenge models under realistic conditions.
- Workflow customization: From reviewer roles to escalation protocols, Ango Hub offers flexible pipelines tailored to enterprise red-teaming objectives.
- Robust safety audits: Built-in capabilities enable teams to run recurring audits focused on tone, subtext, and alignment across sensitive or regulated outputs.
These red-teaming workflows are tightly integrated into iMerit’s broader Generative AI solutions, which span the full model lifecycle—from alignment to fine-tuning and post-deployment evaluations. By embedding expert-in-the-loop (EITL) processes into platforms like Ango Hub, we help teams go beyond automated filters and bring human judgment into model oversight, where tone, safety, and emotional trust matter most.
iMerit’s work in Generative AI spans the full development lifecycle, from pretraining to alignment, fine-tuning, and post-deployment monitoring. Our teams support a wide range of applications, including:
Together, these features enable a human-in-the-loop feedback loop that supports RLHF, fine-tuning, and post-deployment monitoring. But automated tools alone can’t catch all vibe failures. The nuances of tone, implication, and cultural resonance demand expert human reviewers—what we call Expert-in-the-Loop (EITL). These experts bring:
- Sociolinguistics and discourse analysis to detect subtle tone shifts and implications
- Domain-specific ethics ensuring contextual appropriateness across industries like healthcare, law, and finance
- Bias and fairness frameworks to recognize stereotyping, exclusion, or offensive subtext
At iMerit, our expert annotators play a central role in the red-teaming loop, evaluating AI outputs not only for factuality but for tone, safety, and emotional resonance. This expert-in-the-loop process is integrated directly into platforms like Ango Hub, enabling scalable collaboration, disagreement resolution, and multilayered annotation across varied prompts and outputs.
It’s how we translate human judgment into structured insights, ensuring generative AI systems don’t just function, but resonate and align with human expectations.
Conclusion
As GenAI becomes ubiquitous, alignment challenges aren’t disappearing; they’re evolving. Vibe hacking is a glimpse into this next frontier, where tone, implication, and emotional manipulation can subtly derail model behavior. Tackling these nuanced threats demands more than just smarter models; it requires smarter red-teaming, robust workflows, and skilled human oversight.
iMerit is partnering with AI leaders to stay ahead of the curve. With world-class annotation teams and cutting-edge tools like Ango Hub, we help ensure your models remain aligned, reliable, and ready for real-world deployment.
Explore how iMerit can strengthen your GenAI alignment strategy.